Kingdom – Today, scientists divide organisms into five mane groups called kingdom. These states named Monera, Prista, Fungi, Animalia, and Plantae. Examples of beings related to these states are as follows:
Kingdom Come Living Out Of Touch
Previously, living organisms divided into two states: The plant kingdom includes bacteria, fungi, algae, and plants.
The animal kingdom consists of single-cell preferential and cell-free animals.
Some biologists disagree with the classification of bread molds, yeast, and mushrooms. Fungi are similar to plants in many ways.
But the fungus is heterotrophic. They break down the surrounding material and absorb food. This food used for energy and structural materials. The main structural component in their cell walls called chitin.
Therefore, the fungus given an independent state. The taxonomy system lasted for many years. During this period, the people tried to add a third kingdom. By 1969, the world had developed a taxonomy system that adopted five currently living biological states.
Each of the five states represents a group of living things with common characteristics. The common features of the classification system of the five states are as follows:
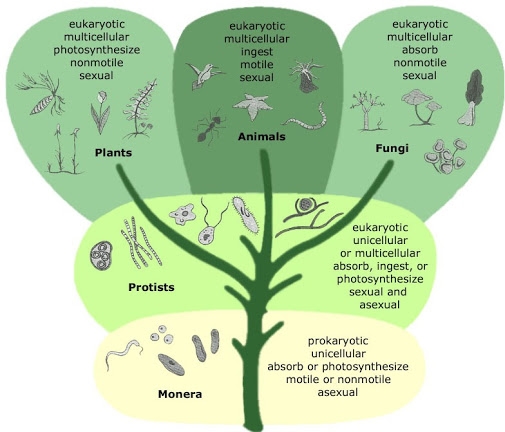
Classification of Five-Kingdom
Kingdom Monera
It consists of prokaryotes, that is, they made up of prokaryotic cells. Brown algae are unicellular, although some types form cell chains or colonies. Prokaryotic cells are completely different from eukaryotic cells. Most are heterotrophic, but some perform photosynthesis because they contain chlorophyll in the cytoplasm. In this kingdom, there are two different organisms, bacteria, and cyanobacteria.
Kingdom Protista
It consists of eukaryotic single cells and simple multicellular organisms. There are three main creatures.
Algae single-celled, colonized, or simply multicellular. They are similar to planting in chloroplasts with cell walls and chlorophyll. Simple multicellular means that they do not have multicellular organs and do not form embryos in their life cycle.
Protozoa are similar to animals, whose cells lack chlorophyll and cell walls.
Some organisms are fungus-like. …
Kingdom Fungi
It includes eukaryotic multicellular heterotrophic organisms that absorbed in nutrients, such as mushrooms. Most fungi are decomposers. They live on organic materials, secrete digestive enzymes, and absorb small organic molecules formed by enzyme digestion.
Kingdom Plantae
This includes eukaryotic multicellular autotrophs. Plants are self-supporting in nutritional mode and make their own food through photosynthesis. Their life cycle consists of multicellular organs and embryos. Moss, ferns and flowering plants included in this state.
Kingdom Animalia (animals)
This includes eukaryotic multi-cellular consumers. The existence of animals is mainly through ingestion of food and digestion in a particular cavity. They have no cell wall and show movement. 5 states features
One biologist believes that the Protista kingdom evolved from Monera, and then caused three other eukaryotic states, namely fungi, plantae, and anemia (animals).
Virus status
Anion viruses have only protein, and viroid’s have only spherical RNA. Both particles can cause infectious diseases in some plants.
Viruses are on the verge of survival and conscience. Due to their crystal nature, they considered lifeless. They are cell-free, that is, they have no cellular organization, but still show some characteristics of living organisms (for example, they have DNA).
Viruses contain RNA or DNA, usually wrapped in a protein shell. They breed only in living cells, where they cause various diseases. They do not considered as organisms and therefore not included in the five-country classification system.
Viruses and viroid’s also have cell-free radicals and not included in the five kingdoms classification system.
You Might Also Like:
- Algae: Its Characteristics and Classification
- Slime mold: Structure and Its Types
- Nostoc structure: important and reproduction