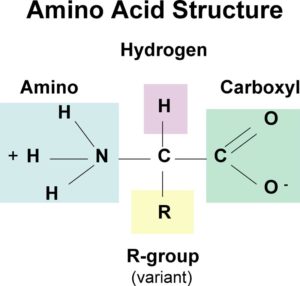
Inorganic molecules made up of amino acids are called amino acids. A basic amino acid is called a -NH2 amino acid, an acidic carbohydrate group is called a -COOH carbohydrate, and an organic group is called a R (or side chain). When amino acids are referred to as -amino, they are carboxylic acids. Carbon (C) is an atom that is found in the middle of each protein. A carboxyl group and an amino group are both carbon-based molecules. In most cases, the last two bonds of a -carbon atom are filled with hydrogen (H) and the R group.
Amino Acid Structure Chart IMG
An amino acid has three parts: a carboxyl group, an aminol group, and an R group on the side chain. There is a carbon atom connecting all of these groups.
Types of Amino Acids List
Here is a list of Amino Acids which is in the List.
- alanine – ala – A
- arginine – arg – R
- asparagine – asn – N
- aspartic acid – asp – D
- cysteine – cys – C
- glutamine – gln
- glutamine – gln – Q
- glutamic acid – glu – E
- glycine – gly – G
- histidine – his – H
- isoleucine – ile – I
- leucine – leu – L
- lysine – lys – K
- methionine – met – M
- phenylalanine – phe – F
- proline – pro – P
- serine – ser – S
- threonine – thr – T
- tryptophan – trp – W
- tyrosine – tyr – Y
- valine – val – V
Classification of amino acids on the basis of R-group
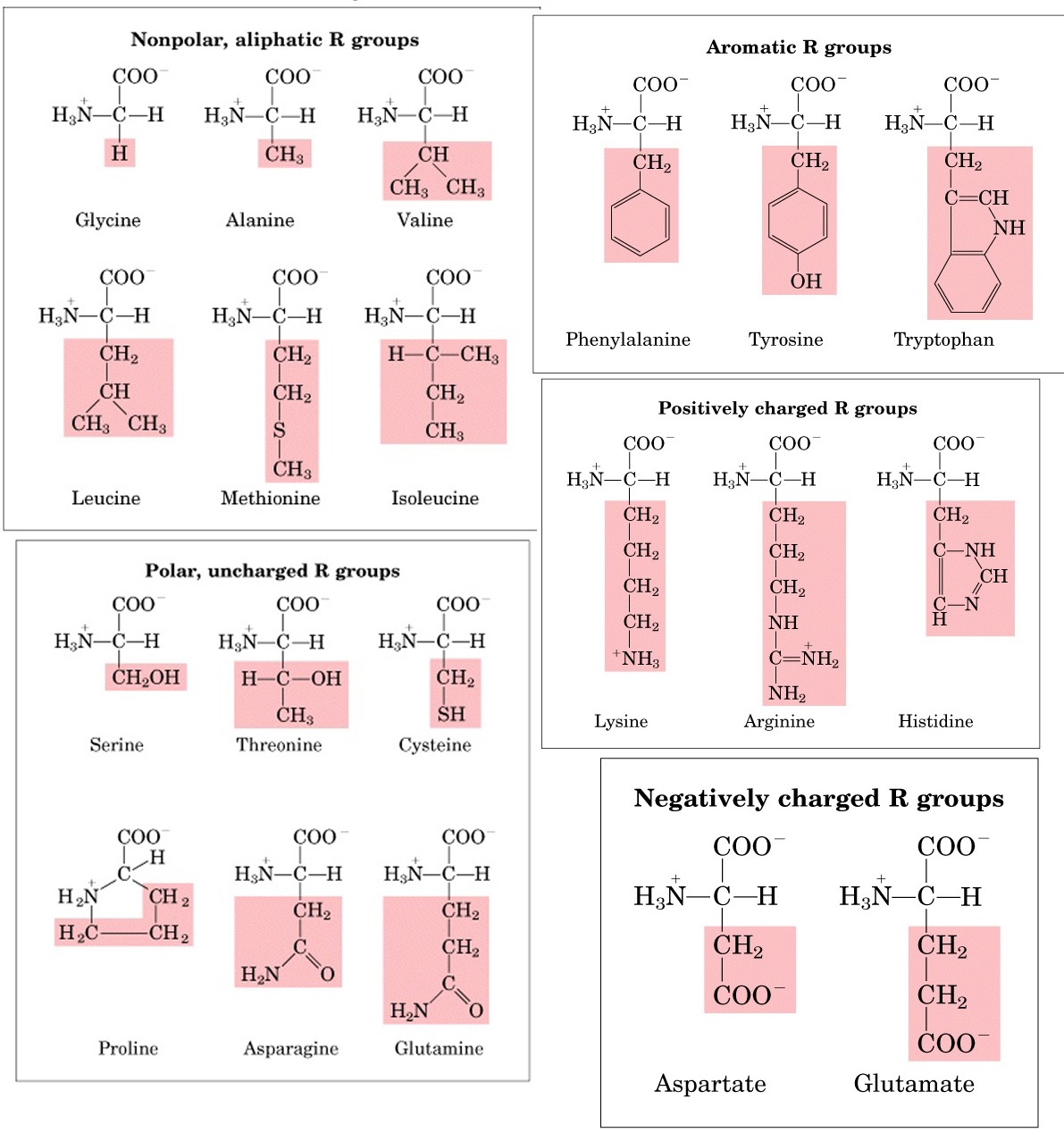
- Non-polar, aliphatic amino acids: Amino acids with nonpolar and hydrophobic R groups are included in this group. In addition to Glycine and Elenin, there are Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, and Proline as well.
- Aromatic amino acids: Phyllalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan are highly hydrophobic amino acids, as are their aromatic side chains. It is possible for anyone to participate in hydrophobic interactions.
- Polar, In addition to being hydrophilic, polar amino acids are more soluble in water than non-polar amino acids. As a result, they form hydrogen bonds with water due to their functional groups. There is a wide variety of amino acids in these classes, including seraine, threonine, cysteine, asparagus, and glutamine.
- Acidic amino acids: An amino acid with an R-group has either an acidic or a negatively charged charge. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid
- Basic amino acids: An amino acid with an R-group has a positive charge or a basic charge. There are three amino acids in the body: lysine, arginine, and histidine.
Classification of amino acids on the basis of nutrition
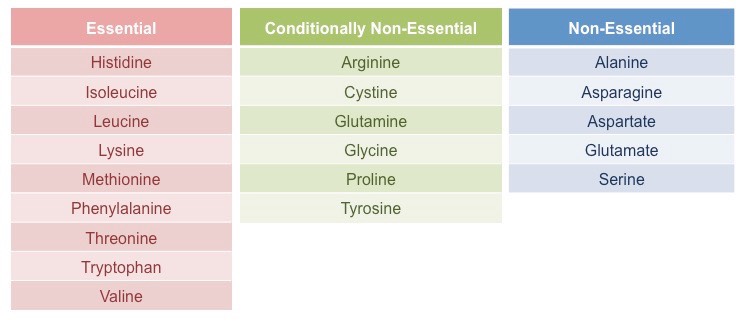
Amino Acids Essential types
It is necessary to obtain nine different kinds of amino acids from food in order to synthesize proteins. The body cannot produce nine different kinds of amino acids, so food must provide these amino acids.
Amino Acids Non-essential
There is no need for food to provide certain amino acids, since the body can produce them naturally.