Many types of laboratory apparatus are used in different experiments, research, and scientific investigations. Some of the most common laboratory apparatuses and their uses are:
Common Laboratory Apparatus
Beakers: Beakers are cylindrical containers with flat bottoms and a lip or spout for pouring. They are used for mixing, heating, and measuring liquids.
Erlenmeyer Flask: Erlenmeyer flasks are conical-shaped containers with a narrow neck and a flat bottom. They are used for mixing, heating, and storing liquids.
Test Tubes: Test tubes are cylindrical containers with a rounded bottom and an open top. They are used for holding and heating small amounts of liquids and conducting experiments on small specimens.
Graduated Cylinder: Graduated cylinders are tall, narrow containers with a spout and a scale printed on the side. They are used for measuring the volume of liquids.
Pipettes: Small, thin tubes that transfer small amounts of liquids from one container to another.
Burettes: Burettes are long, thin tubes for dispensing precise amounts of liquids.
Funnel: A funnel is a cone-shaped device that transfers liquids from one container to another, often to prevent spillage.
Microscope: A microscope is a device that magnifies and observes small objects or organisms.
Petri dish: A Petri dish is a shallow, circular dish used for growing cells, bacteria, or other microorganisms.
Thermometer: A thermometer is a device used for measuring temperature.
Bunsen Burner: The Bunsen burner is a heat source or mechanical device, it must be absolutely safe when using the Bunsen burner.
Laboratory Instruments And Their Uses With Pictures
Bunsen Burner
The use of Bunsen burners in the laboratory is related to combustible gases. Typically, a knob used to adjust the gas flow, and an axle ring used to control the gas flow. Both the knob and the collar must adjusted so that the hot object produces a good flame.
Tripod stand

Usually made of stainless steel or aluminum with three supporting legs. Place the device on the tripod to warm up. During the experiment, mainly used to support or fix beakers or flasks. Due to its height, the Bunsen burner is located under the tripod.
50 common laboratory apparatus their uses
1.Wire Gauze

A piece of iron wire with asbestos pasted in the middle. Place it on the tripod so that the flame does not touch the glass apparatus directly, which will reduce its risk of breaking.
2.Test Tubes

A test tube glass with one end closed and the other open. The closed-end is round. The laboratory uses test tubes to hold small samples. These mainly used for qualitative comparison and evaluation. Biochemistry is a very common phenomenon in the laboratory using a test tube to visualize a laboratory test tube. When a large number of samples need to be compared and tested, these test tubes used to simplify operations. They are also easy to cover or cover with glass or rubber stoppers.
Safety tips: Do not heat test tubes with or without caps
3.Beakers

Beakers very common laboratory instrument and widely used as reaction vessels in laboratories. Used to hold liquid and solid samples, or to collect liquids from various titers or to filter through filtration operations.
In most laboratories, the beaker is simple. Used for heating, stirring, and mixing chemicals. Most beakers have a spout at the rim, which easily inserted into the beaker for laboratory purposes. They usually have lips around their edges and have scars to measure the amount of liquid contained. They are not suitable instruments for measuring liquids. Depending on the size, different types of beakers can used, such as 50cm3, 100cm3, 250cm3, or 500cm3.
4. Titration Flasks
Its called Erlenmeyer flask. The Erlenmeyer flask invented in 1861. Its neck is very thin and widens at the bottom. This makes the flask easier to rotate and mix without the possibility of overflow. The narrow opening also allows the use of glass or rubber plugs. Comfortably affixed to the ring frame and easily shaken or heated. Titration bottle
Again, the side numbers are mainly for estimation rather than accuracy.
An important safety note is not to heat the flask after its capped. This can cause pressure to build up, causing an explosion.
5.Funnels
The laboratory funnel similar to any other funnel but specifically designed for use in the laboratory. Made of glass or plastic and have long or short stems depending on the purpose. Many sizes have chosen, depending on the amount of liquid that needs to pass through the funnel easily and quickly. Funnel sizes are 3 cm, 5 cm, 8 cm, and so on.
6.China Dish

Small plate made of porcelain, which used to evaporate and concentrate the dilute solution. It has different sizes.
7.Measuring Cylinders

For any liquid volume, it is an essential measurement device. There are many special markings above and below the entire length of the container. The measuring cylinder comes in many sizes. The smaller their size or diameter, the more accurate the measurement is. Measuring cylinder
When you look at the volume of a graduated cylinder, you will think that the liquid appears to be slightly sunken. The liquid around the edge of the measuring cylinder will be higher than the liquid in the center. Its called meniscus. To properly read the volume, place the cylinder on a level surface.
Different sizes of 5cm3, 10cm3, 20cm3, 50cm3, 100cm3 and 1000cm3 are also available.
8.Volumetric flasks

A volumetric flask is a round flask that has a flat bottom and a long neck. Volumetric flasks used to measure the precise volume of liquids. Small line on the neck, suggesting how far the flask filled. Provide a special bottle cap that will not allow anything inside and outside the flask.
They have different sizes, namely 100cm3, 250cm3, 500cm3 and 1000cm3.
9.Buret
Burettes commonly used to add precise and precise volumes of liquid. With the help of a diuretic, you can measure or determine the amount of liquid up to 0.01 ML. Its usually fixed on the ring frame by clamps. Diuretics are also like glass tubes. It opens from the top and has a narrow pointed shell at the bottom. Just above the bottom opening, there is a plug valve.
10.Pipettes

A variety of pipettes designed to achieve any specific goals. However, both of these used to measure the exact amount of liquid and then pour the liquid into other containers.
Commonly available sizes are 10cm3, 20cm3 and 25cm3.
11.Thermometer
Use a thermometer to measure the temperature of the substance. The temperature in the laboratory usually measured in degrees Celsius (.C).
12.Watch glasses

The clock glass is just a little convex round glass. It can hold small amounts of solid or liquid. Watch glass used for evaporation and can also used as a beaker lid.
13.Iron stand

A typical retort frame has a heavy base and vertical rods, usually made of metal. Many devices (such as various types of clamps and iron rings) can fixed from thumb to pole without using any height and orientation to support the target device.
14.Wash Bottle

Nowadays, polyethylene washing bottles used in laboratories to store distilled water for various operations, such as transferring sediment from containers to filter paper or washing off sediment. When you press the bottle with your hand, the water will flow out of a tube.
15.Florence Flask

Its called a boiling flask. Under the Florentine flask is a round neck. Its used to hold liquid and is easy to heat and penetrate. Easily covered with a glass or rubber stopper.
Once again, safety requires that the flask never heated when its capped or capped. This can create pressure and cause an explosion.
16.Test tube stand
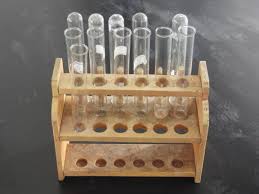
Its made of wood, polyethylene, or steel, and the test tube placed directly over it. Test tubes usually placed in a test tube rack. The test tube rack specifically designed for this purpose. If these test tubes exposed to bare hands (in case of heat or other reasons), use a test tube clamp to move them.