All Magnetic Types Materials and substances have some sort of magnetic properties that are further described in the article. The term “magnetic materials” is used to describe only ferromagnetic substances ( the description is below) However, all materials can be classified in the different categories based on the magnetic properties that they display:
Types of magnetic materials
- Paramagnetic materials
- Diamagnetic materials
- Ferromagnetic materials
- Ferrimagnetism
- Antiferromagnetism
Here we discuss briefly these types of magnetic materials

Paramagnetic materials
Materials that aren’t magnetically attracted referred to as paramagnetic materials. For example: aluminum, tin magnesium etc. Their relative permeability can be small however, it is still positive. As an example, the permeability of aluminum is 1.00000065. The magnetization of these materials occurs only when they placed in a powerful magnetic field. They also move according to the field’s direction.
Paramagnetic materials possess individual atomic dipoles that are oriented in random order as follows:
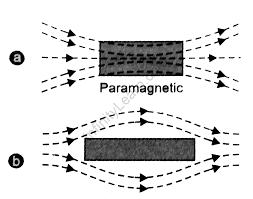
The magnetic force that results is zero. If a powerful magnetic field from outside is applied, the permanent magnetic dipoles align themselves in a parallel direction to the magnetic field, leading to a positive magnetic field. Because the position of the dipoles in parallel to the magnetic field isn’t complete and the magnetic field is tiny.
Diamagnetic materials
Materials that pulled by magnets, like zinc. Lead, mercury sulfur, copper, bismuth, bismuth and silver and so on. are called diamagnetic substances. Their permeability is lower than one. As an example, the permeability ratio for bismuth is 0.00083 and copper can be 0.000005 as is wood 0.9999995. They are mildly magnetic when placed in a string-like magnetic field. They also move in a direction that is opposite to the direction of the magnetic field.
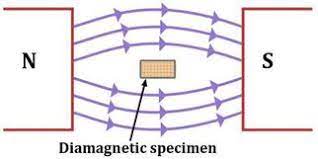
In diamagnetic materials, the two magnetic fields that are relatively weak created by the orbital revolution as well as the axial movement of electrons around nucleus is in opposing directions and are in complete opposition. Permanent magnetic dipoles do not exist in these materials. Diamagnetic materials are very limited to have none applications in electrical engineering.
Ferromagnetic materials
The substances that are attracted by magnetic fields or magnet is called ferromagnetic materials, for example nickel, iron, steel and cobalt. The permeability of these materials is extremely high (that can be as high as thousands or hundreds of hundred).
The opposing electromagnetic effects caused by electron orbital motion as well as electron spin don’t completely eliminate one another in an atom in such a material. There is a significant contribution from every atom, which assists in the formation in the formation of an inner magnetic field such that when the substance put in the field of magnetic energy, its value increases by many times the amount that was in the space free before the material put in.
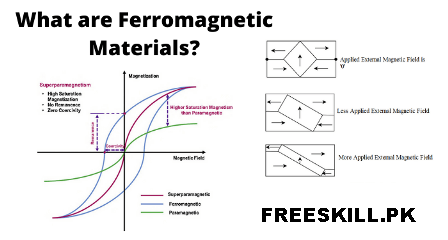
In the context of electrical engineering, it is enough to categorize materials as ferromagnetic non-ferromagnetic ones. These include materials with a relative permeability nearly equal to unity whereas the former are those with relative permeability much higher than unity. Diamagnetic and paramagnetic materials are included into the non-ferromagnetic material.
Ferrites
Ferrites distinct category of ferromagnetic material which located in an intermediate space between non-ferromagnetic and ferromagnetic materials. They comprise extremely small particles of a ferromagnetic material with a high permeability, and bonded by binding resin. The magnetization that ferrites produce is sufficiently large to have commercial value however their magnetic saturation is not as great as that of ferromagnetic substances. Ferrites could be either hard or soft ferrites.
There are two Main Major Types of farrties
Soft Ferrites
Ceramic magnets, also known as ferromagnetic ceramics are composed of iron oxide, Fe2O3, which is a mixture of some divalent oxides such as MnO, NiO or ZnO. They feature a hysteresis loop that is square and their high resistance and demagnetization appreciated in computer machines where high resistance is required. The major benefit for ferrites lies in their resistance. Commercial magnets can have a resistivity up to 109 ohms-cm. Eddy currents caused by the alternating field are diminished to a minimum and the use of these magnets is expanded to higher frequencies , including microwaves . Ferrites made through the mixing of powdered oxides and compressing them and sintering them high temperatures. High-frequency transformers used in televisions and Receivers with frequency modulation nearly always constructed from ferrites as cores.
Hard Ferrites
They are permanent magnetic ceramic materials. The most significant group of ferrites that are hard is the fundamental composition of MO.Fe2O3 in which MO is barium(Ba) Ion and strontium (Sr) Ion. They have a hexagonal design and are inexpensive in price and density. Hard ferrites utilized in relays, generators, and motors. Electronic applications use magnets to power loud speaker, telephone ringers and receivers. They also serve as the holding devices of door closers seals, latches, seals and in a variety of toy designs.
DNA Ball: Describe its shape and Purpose?