What is Electronics Microscope?
In order to get a deeper knowledge of structure in little time, light microscopes were replaced by electron microscopes. High magnifications of objects do not compromise the optics’ ability to resolve fine detail, since the resolving power may reach through. In order to look into the submicroscopic structure and get a better knowledge of cytology, we may use an electron microscope, which can offer a clear picture of an item that is magnified 500 times, including 3D pictures (scanning electron microscope). Let surface granularity to shine through. We can calculate its dimensions and form from the photo.
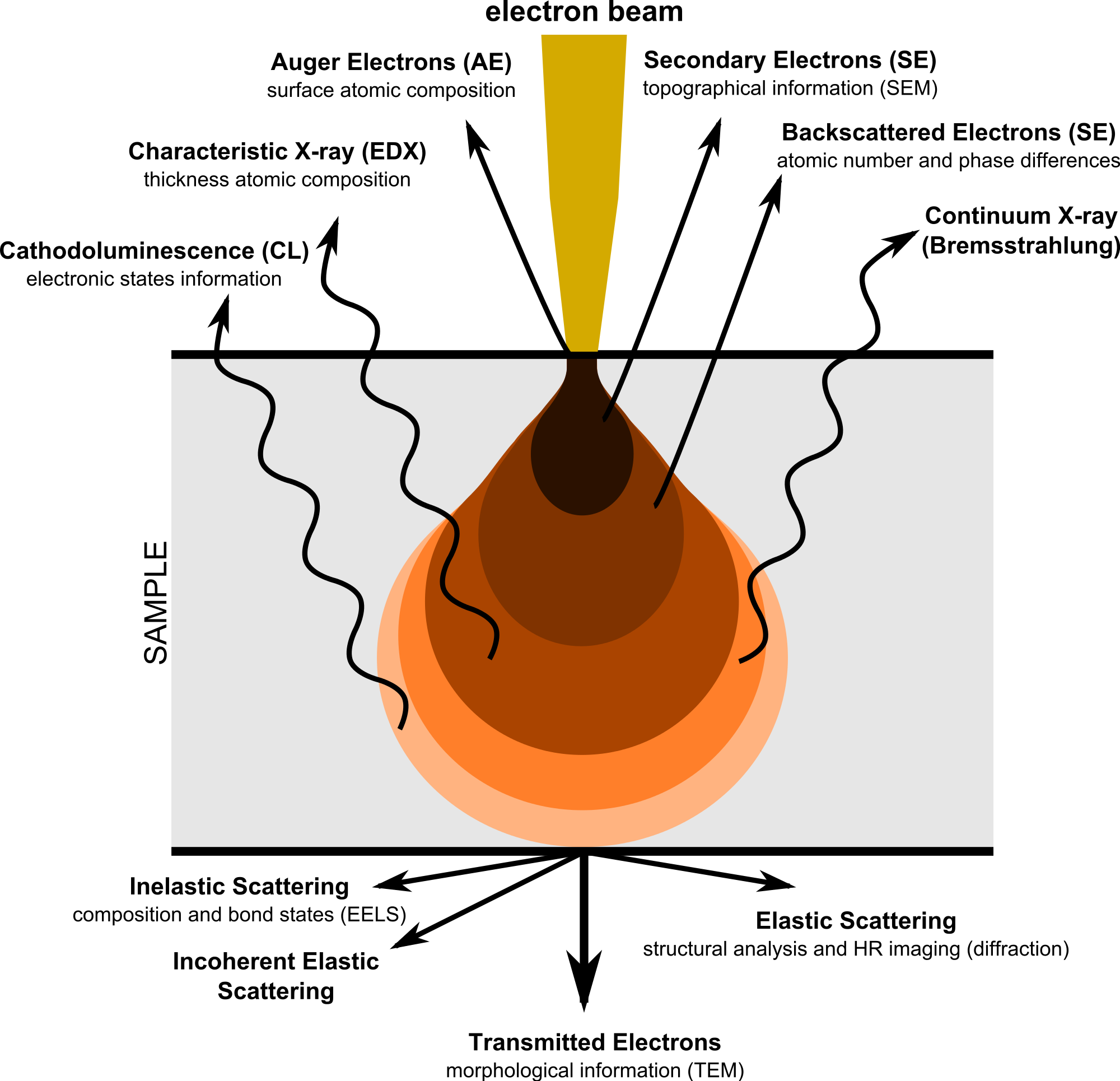
Give one difference in resolution and magnification in microscopy
Resolution is the degree to which two things may be recognized from one another (Separate objects that are close together). The quality of the lenses and the frequency of the light source are crucial factors. The resolution magnification the number of times the picture expanded than the specimen is, improves as the wavelength decreases. The lenses’ strengths and their combinations determine the outcome. An enlarged picture with no further information.
How Does An Electron Microscope Work
High-resolution pictures of biological and chemical substances may be obtained using electron microscopy (EM). Tissues, cells, organelles, and large-molecule complexes are all objects of investigation in biomedical research using this method. Electrons (extremely short wavelengths) are used as a source of illumination radiation, which contributes to the great resolution of EM pictures. Many complementary methods (splitting, immunomodulating, and negative staining) are used to an electron microscope in order to provide answers to research issues. The structural foundation of cell disorders may be gleaned from EM pictures, as can some fundamental information about how cells behave.
Types Of Electron Microscope
There are two main types of electron microscopes – The electron microscope may be either an electron microscopy (TEM) or a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Electron microscopy is a technique used to observe the predicted picture produced by passing electrons through thin materials (tissue slices, molecules, etc.). There are numerous similarities between TEM and common (compound) optical microscopes. TEM is often used to examine the organization of protein molecules in cell membranes (produced using negative staining methods), the structure of proteins (in contrast to mineral colors), the molecular modulation of cellular structural viruses, and the anatomy of capillaries and blood vessels (breaking freezing).
You Might Also Like:
- What is Microscope Describe the Parts And Function
- What is cell: Describe the structure of a plant cell?