What is the carbon cycle?
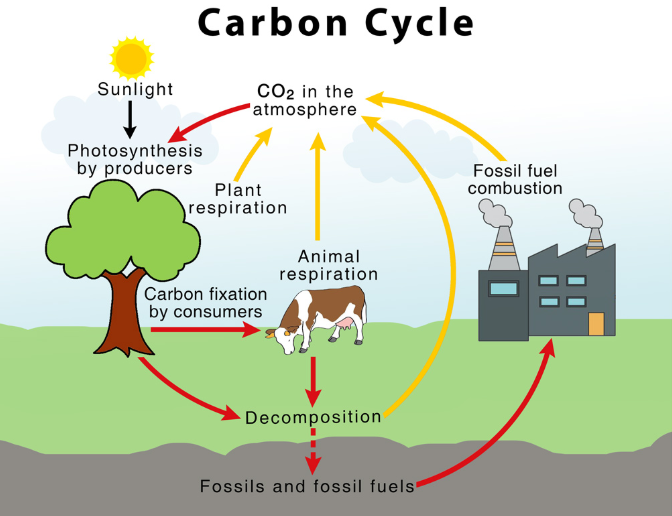
Organic compounds contain carbon dioxide (CO2) in the air and HCO3 oxide and CO3 in the carbon source of water. Green plants take carbon dioxide from the air and use it in photosynthesis to make glucose and other carbohydrates. Marine plants use CO2, HCO3 and CO3 ions dissolved in water. Plants use food (glucose) for their growth and development. Animals also get food from plants these are called carbon cycle.
Food energy (glucose, protein, or fat) is released by living things through respiration or decomposition. This energy is used by treated glucose and oxidation to release CO2. Plants used this carbon dioxide again during photosynthesis and completed the cycle.
Carbon atoms are the main components of many biological molecules. Carbon is found in graphite and diamonds in nature. It looks like carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Explain Carbon Cycle With Diagram
Importance and uses of Carbon Cycle in our Daily Life
The carbon cycle is an ideal cycle, and in some sense, once the carbon is removed, it will return to the atmosphere.
The main source of carbon in the life world is carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and water. Fossil fuels such as peat, coal, natural gas, and oil also contain carbon. The carbonates in the Earth’s crust also produce carbon dioxide.
The main process of bringing carbon from the atmosphere or water to the living world is photosynthesis. Producers absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into organic compounds. In this way, carbon becomes part of the main body of the product. This carbon enters the food chain and passes into herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers.
The breaths of producers and consumers return carbon dioxide to the environment. The analyst will also analyze organic waste and dead bodies, which are released. Burning wood and fossil fuels also add large amounts of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
Human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels have disrupted the carbon dioxide balance. As a result, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases, which leads to the effect of global warming and global warming. Carbon cycle
Of all the known chemical elements of mankind, perhaps the most interesting element is carbon. For example, did you know that one of our most valuable gems, diamonds, is presented to us as crystals? As with graphite, carbon forms lead from lead in the pencil. Coal is the source of most heat and power in the machine age, especially carbon.
But most importantly, carbon is vital to life. The bodies of all living things are made up of compounds that contain carbon. In fact, scientists believe that wherever there is any amount of carbon on Earth, their lives may already be there.
The carbon cycle refers to the process by which carbon is removed, used, and constantly replaced by living organisms. Here’s how it works. Carbon dioxide is in the air. Plants take carbon from this gas and use it to build roots, stems, and leaves. Animals obtain carbon for food from plants in the form of plants, fruits, or grains. At the same time, carbon dioxide returns to the air through the air or burning or decomposing plants. This completes the carbon cycle.
When elements are combined, we form a compound. So far, the number of carbon compounds we know is over 200,000! All other elements together make up a small number of compounds such as one carbon element. The reason for this is that carbon atoms can join with the atoms of other elements in many different ways, and they can combine with other carbon atoms to form rings and chains.
You will constantly be exposed to or used carbon compounds in your daily life. You will inhale a small amount of carbon dioxide and release more gases. Most fuels, foods, medicines, plastics, and perfumes (and dozens of other products) are carbon compounds!
You Might Also Like:
- Sixth Sense: Theories, Researches, and Results
- Mechanism of Ion Absorption by Roots
- Factors Affecting Absorption of Water By Plants