Define Mitochondria
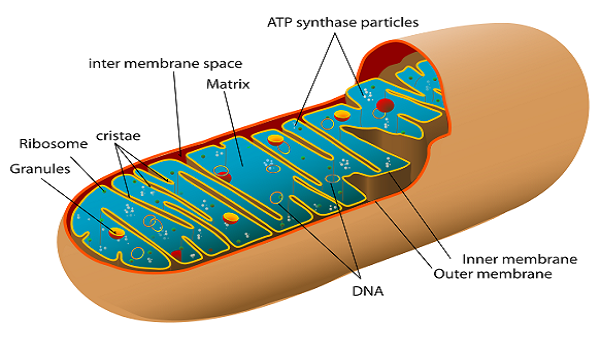
Mitochondria are the cellular powerhouses responsible for metabolizing food into usable energy. The citric acid or Krebs cycle produces energy, and it happens in the matrix. DNA from the ribosome and mitochondria are both found in the matrix, which is a thick, sticky material.
Mitochondria Structure
Functions of Mitochondria
Citric Acid Cycle
During oxidation, pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA, which then undergoes further metabolic to produce carbon dioxide, NADH, and FADH2. Transferred fatty acids are metabolized to acetyl-CoA in the mitochondrial matrix before entering the citric acid cycle. Next, the electron transport chain inside the inner mitochondrial membrane uses NADH and FADH to produce enough ATP for the cell.
What is the function of cristae in mitochondria?
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA is included in the matrix as well, giving the mitochondria a degree of autonomy. Mitochondrial DNA is circular, like bacterial DNA. It has just 37 genes, some of which code for DNA RNA genes and others for enzymes involved in ATP synthesis (the cellular energy molecule).
Nuclear DNA, rather than mitochondrial DNA, encodes the vast majority of the proteins necessary for cellular respiration and ATP generation. Mutations in mitochondrial genes may result in a wide range of illnesses, including blindness in humans in the form of Leper genetic optic neuropathy.
Mitochondrial RNA
All of the machinery required to convert the mitochondrial DNA into proteins is housed in the mitochondrial matrix. RNA (transfer RNA, ribosomal RNA, rRNA) is the genetic material that is translated into ribosome molecules or complexes. This RNA employs a variant of the genetic code used by cytoplasmic RNA. Just around 22 R-R are encoded by the mitochondrial DNA, yet they are the only RNAs capable of translating mitochondrial RNA (M RNA) into proteins.
Matrix Proteins
The mitochondrial matrix contains proteins that were encoded by nuclear genes rather than mitochondrial ones. Transported proteins in the matrix originate in the cytoplasm and cross both the outer and inner membranes. Some of these proteins are involved in the electronic transport chain of the inner mitochondrial membrane, while others are part of the ribosome or are necessary for replication and transcription inside the mitochondria.
| function of outer membrane in mitochondria |
| what is cristae in mitochondria |
You Might Also Like:
- What is Cell With a Membrane & Nucleus
- Different Types of Molecules Which explained with Examples
- How far the electron microscope, increase the structures and functions of the organs?
- What is cell: Describe the structure of a plant cell?