“An organelle’s nucleus is separated from its surroundings by nuclear membranes that are multilayered“
What is the Nuclear Membrane?
DNA is stored in the nucleus of all eukaryotic cells including those in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Nuclear envelopes and membranes, known as nuclear membrane, surround and cover every nucleus. Nucleoplasm (the fluid within the nucleus) and cytoplasm are separated by this membrane.
Nuclear Membrane Structure
Inner and outer membranes make up nuclear membranes. Bilayers of phospholipids are found in both membranes. There are four series of phospholipids in the complete nuclear membrane.
Inner and outer membranes are separated by the perinuclear space. It is composed of rough endoplasmic reticulum that works on the outer membrane. Transport of proteins is carried out by this organelle.
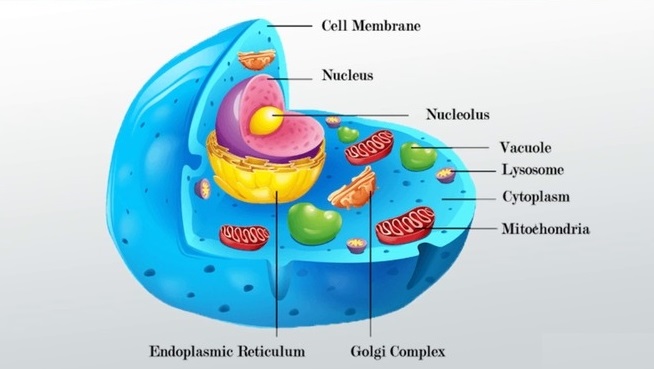
Parts Of Nuclear Membrane
Cell nucleus are surrounded by the nuclear membrane, which consists of the following components:
Outer Membrane
It consists of two layers of lipid molecules. Liposomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum in the outer layer, which is composed of lipids.
Inner Membrane
A DNA chain is formed by proteins that rearrange the nucleus and maintain the genetic material in its correct position. An inner membrane is enclosed by a nuclear lamina that connects proteins and fibres. The nucleus is supported structurally, DNA is repaired, cell cycle events such as cell division are controlled, and the replication of DNA is also facilitated.
Nuclear Membrane Function
Nuclear membranes perform the following important functions:
- There are tiny holes in the nuclear envelope known as nuclear pores. Flow of material between the nucleus and the outside is made possible by the pores. The inner membrane is also connected to the outer membrane.
- Nuclear pores are doubled during the interphase part of cell division due to the expansion of the nuclear envelope’s surface.
- Water, ions, ATP, and small molecules can pass freely through the nuclear membrane due to its double membrane by pores that help control macromolecule crossing such as proteins and RNA. The macromolecules conduct information through the membrane of the cell.
Difference Between Nuclear Membrane in Plant and Animal Cells
Plant and animal cells have different nuclear membranes for the following reasons:
| Nuclear Membrane in Plant Cell | Nuclear Membrane in Animal Cell |
| They lack several proteins. | They possess proteins. |
| The centrosome is absent. | The centrosome is present. |
Visit Freeskill.pk Biology or download app for more information on nuclear membranes, their structure, and function.
- Different Types of Molecules Which explained with Examples
- How far the electron microscope, increase the structures and functions of the organs?
- What is cell: Describe the structure of a plant cell?