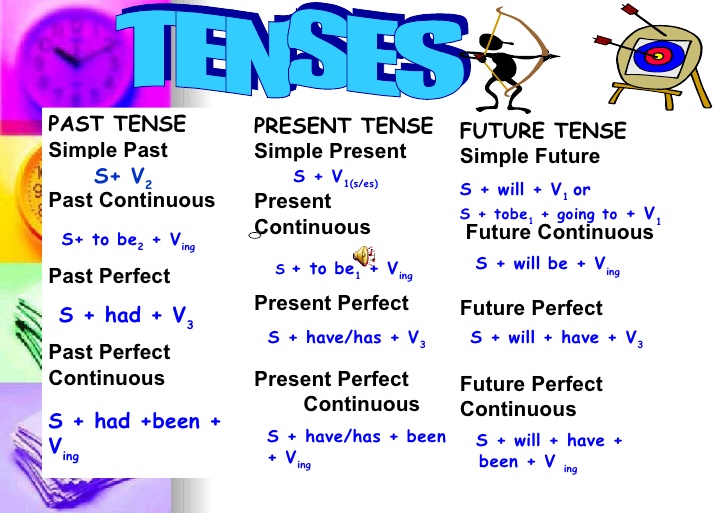
Types of Tense Its examples And Formula
Here we discuss about Types of Tense Its examples. Universally, the time has got three divisions and consequently, there are three tense in English, Present, Past and Future. Each of these tenses is further sub-divided into four categories namely; Indefinite, Continuous, Perfect, and Perfect Continuous. We discuss them in detail.
What Is Tense?
Tense is that characteristic of verbs which indicates the time of the action or of the state of being that is described. In other words, by ‘Tense’ we understand the correspondence between the form of the verb and our concept of time.
Tense Definition And Examples
12 Types of Tenses
Present Indefinite Tense
Present Indefinite (Simple Present) Tense is used:
- To express a single or momentary action in the present time. e.g.
(i) She talks.
(ii) I see a rainbow in the sky.
- To express Habitual action e.g.
I get up every day at 6 O’ Clock.
- To express general truth e.g.
Fortune favours the brave.
- In exclamatory sentences, particularly with words ‘here’ and ‘there’ e.g.
(i) Here comes Ali!
(ii) There she goes!
- In the vivid narrative of the past events e.g.
Sohrab now rushes forward and deals a heavy blow to Rustum.
- To indicate a plan in the near future e.g.
(i) He arrives here next month.
(ii) When does the college reopen?
- To indicate quotations e.g.
Keats says, “A thing of beauty is a joy forever”.
- In clauses of time and of condition, it is used instead of Simple Future Tense e.g.
(i) I shall wait till you finish your lunch.
(ii) If it rains, we shall get wet.
- In commentaries of the sports in progress, it is used instead of present continuous tens e.g.
Shoaib holds fast and Akram drops the catch.
- With the following verbs. Present indefinite is used instead of present continuous.
(a) With the verbs of perception like see, Smell, or with verbs of appearing like the look, seem, appear etc.
(b) With verbs of emotions like love, hate, amuse, desire refuse etc.
(c) With a verb of thinking like suppose, agree etc.
(d) With verbs of possession like have, own, possess consist, contains etc.
Example
(i) I am having a pen. (Incorrect)
I have a pen. (Correct)
(ii) This class is consisting of fifty students (Incorrect)
This class consists of fifty students. (Correct)
Present Continuous Tense
- It is used for an action going on at the time of speaking e.g.
She is singing a song.
- It is used for a temporary action not actually happening at this time of speaking but belongs to present time e.g.
I am reading “War and Peace”.
- It is used for the action planned to take place in future e.g.
My Uncle is arriving here tomorrow, tonight, the next day etc…
- It is used for persistent and obstinate habits with words like always, continuously, consistently etc. e.g.
My dog is very silly; he is always running out into the road.
Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Tense is used:
- To describe past events when we think more of their effect in the present than of their time itself e.g.
I have finished my work.
- To indicate completed action in the immediate past e.g.
He has just gone out.
- To denote an action beginning at some time in the past and continuing up to the present moment’s e.g.
I have known him for a long time.
- To express past actions whose definite tense is not indicated e.g.
I have never known him to be angry.
Note: The indicator words used for present perfect are: just often, never, ever, so far till now, yet, already, since for, always But the same action with the indicator of past time like yesterday, in June, in 1990, at 4 O clock, last week/year in the morning etc. will be expressed in the simple past tens e.g.
(i) I have lived here since 1970. (Present Perfect)
(ii)He has always lived in this town. (Present Perfect)
(iii) He was born in 1960. (Past Indefinite)
(iv) She met me yesterday (Past Indefinite)
But Some Adverbials go with both Tenses
I saw him today
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- It is used for an action which began at some time in the past and is still continuing e.g.
(i) She has been sleeping for five hours.
(ii) They have been playing since the 5’O clock.
Simple Past Tense
- It is used to indicate an action completed in the past and indicated by an adverb, phrases of the past e.g
I received a letter last week.
- Sometimes even without the adverbial, the simple past can be indicated by the context e.g
I did not sleep well.
- It is also used for past habits e.g
She always carried an umbrella.
Past Continuous Tense
- It donates and action going on at some time in the past.
The time may or may not be mentioned e.g.
The Light went out while I was reading.
- It is used for persistent habits of the past with adverbial always and continually e.g.
He was always grumbling.
Past Perfect Tense
- It is used for an action completed before a certain moment in the past e.g
(i)I had met him in Karachi.
(ii) I had seen him last time five years before.
- If two actions happened in the past, the earlier action is used in the past perfect and later in the past indefinite e.g
I had finished my work when Ali comes to see me.
- It is used for conditional sentences e.g.
If he had gone, he would have caught the train.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
It is used for an action that began before a certain point in the past and continued up to that time e.g.
At that time he had been writing a novel for two months.
Simple Future Tense
It is used for an action that is still to take place e.g
I shall see him tomorrow.
Generally, this tense expresses pure and colourless future. When the future is coloured with intention, it is better to use ‘going’ to form reverse used of shall or will.
Future Continuous tense
- It represents an action as going on at some time in future e.g
When I get home, my children will be playing.
- It is used for future events that are planned e.g.
I shall be staying there until Sunday.
Future Perfect tense
It is used to indicate the completion of an action by a certain future time e.g
I shall have written me a book by the end of next month.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
It presents an action being expressed in progress within a period of time that will end in somewhere in future e.g.
By next July, he will have been living there for four years.
What is cell: Describe the structure of a plant cell?
What is Microscope Describe the Parts And Function