Arteries vs Veins – Blood travels via arteries to the body’s extremities and veins to the heart. Blood vessels in the lungs are the only exception; otherwise, arterial blood is oxygenated while venous blood is deoxygenated. Muscle tissue forms the thick walls of arteries. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
Differences Between Veins and Arteries?
Differences Between Arteries vs Veins
| Arteries | Veins | |
| 1. | The pulmonary artery, which carries oxygen – poor blood, arteries transport oxygenated blood. | They transport oxygen-depleted blood to the heart ( except pulmonary vein) |
| 2. | no valves present | valves are present |
| 3. | they can feel a pulse | they can’t feel the pulse |
| 4. | further divided into arterioles. | further divided into venules. |
| 5. | bright red color | dark red color |
| 6. | have elastic walls that expand with a surge of blood | thin and less elastic walls |
| 7. | blood pumped into a single systemic artery called the aorta | blood return via interior and superior venae cavae and coronary sinus |
| 8. | they are very deep and are protected by tissues | they are also deep and superficial |
| 9. | end in blood capillaries | start in blood capillaries |
| 10. | if blood is not present, still they do not collapse or cut across. | collapse when there is no blood in it also can be cut across. |
| 11. | their pathways are fairly distinct | they have numerous interconnections |
| 12. | have predictable drainage or supply | they are just like arteries except for dural sinuses and hepatic portal circulation |
| 13. | the blood pressure inside arteries is high | in veins, the blood pressure is low |
| 14. | they distribute blood to body organs | collect blood from body organs |
| 15. | arteries have small lumen | the veins have a large lumen |
| 16. | sporty or fast movements of blood with giving pulse | they show the sluggish movement of blood |
Difference Between Arteries And Veins
The function of veins is to return blood from the body’s extremes to the heart. Vein blood is deprived of oxygen and contains mostly carbon dioxide outside of the pulmonary veins, which return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. Venous blood is referred to as oxygenated blood. Veins have valves that may halt the blood flow and are broader than arteries. The venous wall is defective.
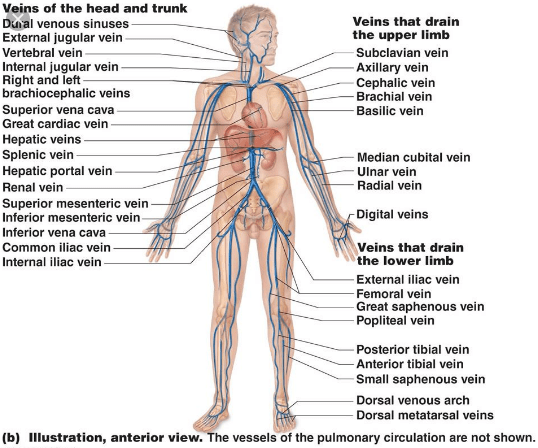
What is a Vein?
Veins are the arteries nearest to the surface that return oxygen-poor blood to the heart. Since veins lack the muscular lining seen in arteries, blood flow is maintained by use of valves. Venules are the smallest blood vessels in the body; when they go closer to the heart, they mature into full-size veins.
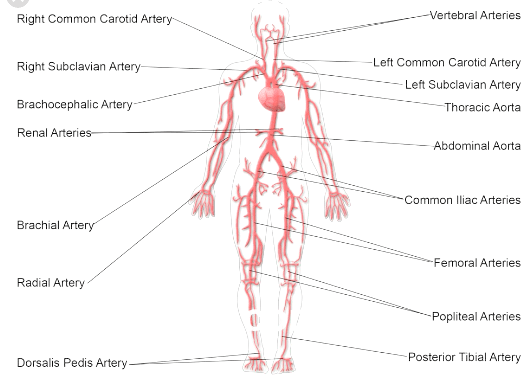
What are Arteries?
The arteries are the channels via which blood travels from the heart to the rest of the body. The pulmonary arteries not only transport oxygen-poor blood to the lungs, but also blood rich in oxygen. There is no valve and the arterial wall is thick.
Conclusion
Arteries, being the veins nearest to the heart, are exposed to the most intense physical pressure as blood is pushed through them. Arteries have strong walls and a pulse that travels through them with each heartbeat. Veins can only bear little pressure, yet they have to fight gravity to return blood to the organs from the heart. Valves prevent the backflow and pooling of blood in many veins, notably in the legs.
See Also:
- RNA: Describe its Structure, Types, & Functions
- Amino Acids: Its Types, Structure, Classification, and Functions
- Enzymes: Its Structure, and Characteristics