What is Fungi?
Multicellular eukaryotes are the norm in the fungi kingdom. They are essential members of ecosystems due to their role in the cycling of nutrients and their status as heterotrophic bacteria (organisms unable to produce their own food). Sexual reproduction in fungi is not limited to mating with other fungi; they may also mate with plants and microorganisms. Yet, they may also cause sickness in animals and plants. mycology The scientific study of mushrooms.
Growing Edible Mushrooms At Home
Types of Fungi
There are five types of Fungi: Zygomycetes, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota and Deuteromycetes. A brief description of each gate given below.
Zygomycetes: Zygomycetes are organisms that result from the union of two or more cell types. The asexual spores are called sporangiospores, while the sexual ones are called zygospores. There are no septa in the hyphae. Case in point: Mucor.
Ascomycetes: Sometimes referred to as “sac fungi,” ascomycetes are a kind of fungus. They may also be decomposers, parasites, or even saprophytes. Ascospores are the sexual spores. Conidiospores are the reproductive organs of asexual fungi. Saccharomyces is a good example.
Basidiomycetes: The fungi of the Basidiomycetes kingdom are generally parasitic, with mushrooms being the most prevalent kind. Basidiospores are sexual reproductive structures. The asexual reproductive mechanisms include conidia, budding, and fragmentation. Agaricus, for instance.
Deuteromycetes: Deuteromycetes are defective fungus because their reproductive process deviates from that of typical fungi. There is no sexual reproduction among them. Conidia play a crucial role in asexual reproduction. As an example, consider the fungus Trichoderma.
Structure of Fungi
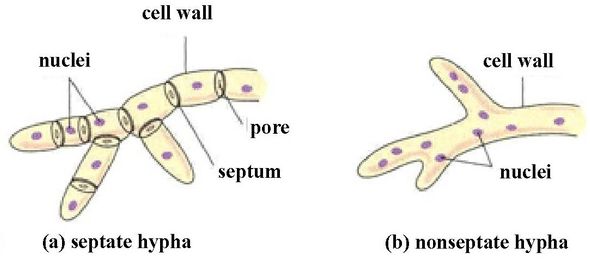
- Except for yeast cells, almost all fungi have a filaments structure.
- They may be either simple or complex, with several cells.
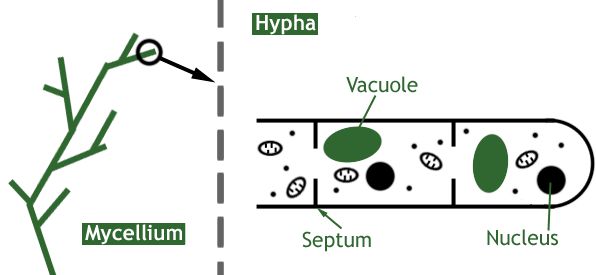
- Hyphae are the long, threadlike structures found inside fungi. Mycelium is the term for the meshlike structure formed by these hyphae.
- Cell walls of fungi are composed of chitin and polysaccharides.
- A protoplast is contained in the cell wall and develops into the membrane, cytoplasm, organelles, and nucleus of a mature cell.
- The nucleus is compact and well-defined, with visible chromatin strands. A nuclear membrane protects the nucleus’s inside.
Fungi Characteristics
- Fungi are heterotrophic eukaryotic creatures with no blood or movement.
- They might have one cell or form long filaments.
- Spores are the method by which they propagate.
- Alternation of generation is a biological phenomena seen in fungi.
- Chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis, which fungi lack.
- Fungal cells use starch as a food storage compound.
- Fungi are responsible for the biosynthesis of chitin.
- Fungi have very tiny nuclei.
- Fungi don’t go through an embryonic period. It’s the spores that cause them to grow.
- Sexual or asexual reproduction is the manner of reproduction.
- Several types of fungus may infect and even kill their hosts.
- Pheromones are chemicals produced by fungus that allow them to reproduce sexually.
- Mushrooms, moulds, and yeasts are all good examples.
See Also:
- Chromosome: Describe its Structure
- Nucleus: Define its Structure & Function
- Cytoplasm: Define Its Function, Structure, and Location