What is a molecule? What are the types of molecule
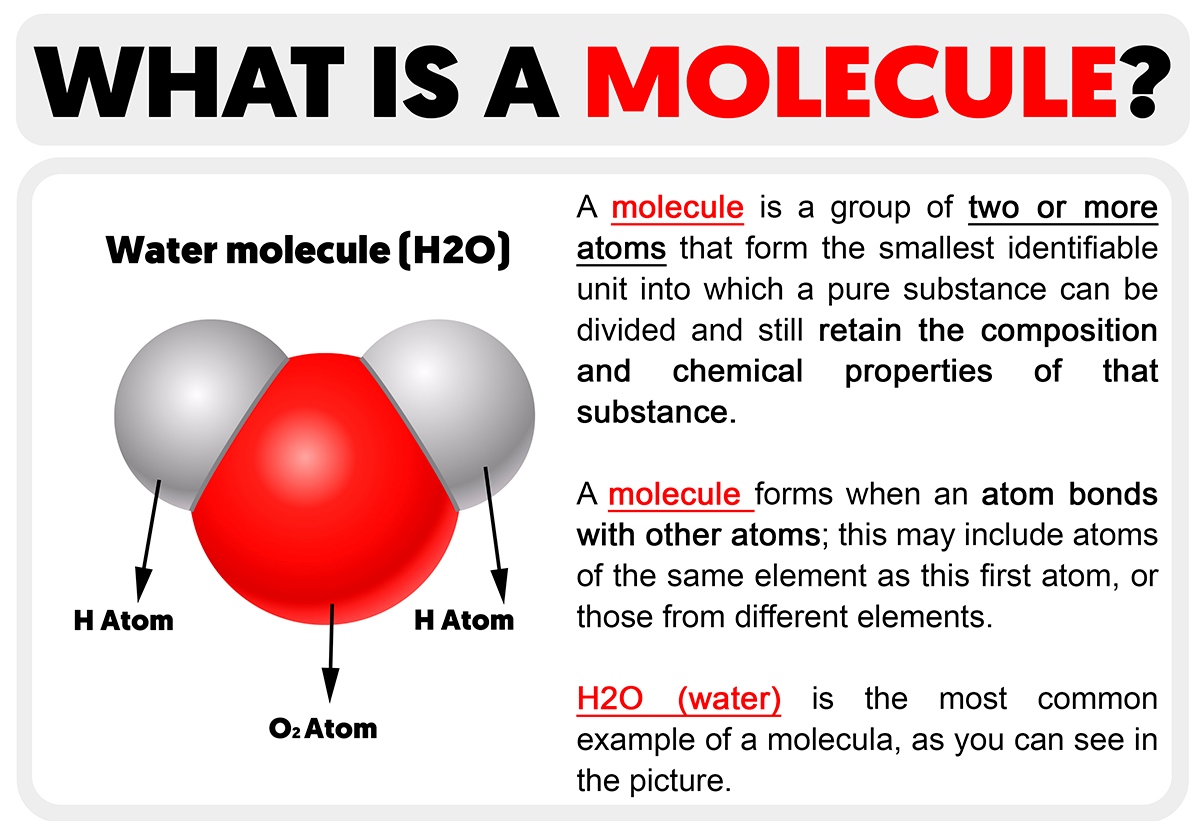
A molecule is a collection of two or more atoms that are chemically bound to one another. They can be identical (such as in an oxygen molecule, O₂) or dissimilar (such as in a water molecule, H₂O). Molecules are the least mass units of a substance that still have its chemical characteristics. The atoms in a molecule are held in place by covalent bonds, where electrons are shared.
Molecules may range in size from a few atoms (such as oxygen, O₂) to huge and complicated structures (such as proteins or DNA).
Molecules can be grouped into various types depending on their structure and composition. Below are the key types:
What are the types of molecule
Elemental Molecules (or Diatomic Molecules)
They contain two or more atoms belonging to the same element. Some common examples are:
O₂ (Oxygen molecule): Two oxygen atoms.
N₂ (Nitrogen molecule): Two nitrogen atoms.
H₂ (Hydrogen molecule): Two hydrogen atoms.
They are usually gases at room temperature.
2. Compound Molecules
These consist of atoms from two or more different elements that are chemically bonded together. Common examples include:
H₂O (Water): Composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
CO₂ (Carbon dioxide): Composed of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
NaCl (Sodium chloride): Composed of sodium and chlorine atoms.
Compound molecules have distinct properties from the elements they are made of.
3. Organic Molecules
These are carbon atoms combined with hydrogen and frequently other atoms such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or phosphorus. Organic molecules typically have a link to living organisms. Examples include:
Carbohydrates: Such as glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆).
Proteins: Composed of amino acids (e.g., hemoglobin).
Lipids: Such as fats and oils.
DNA: An intricate organic molecule that contains genetic information.
4. Inorganic Molecules
These are not based mainly on carbon atoms. Most inorganic molecules are more straightforward and are usually minerals or salts. Some examples are:
H₂O (Water): Even though it has hydrogen and oxygen, it’s not organic.
NaCl (Sodium chloride): A straightforward salt.
5. Macromolecules
These are extremely large molecules composed of repeating units (monomers) and can be organic or inorganic. Some examples are:
Polymers: Chains of small molecules, like plastics or synthetic fibers.
Proteins, Nucleic acids (such as DNA/RNA), and Polysaccharides (such as starch).
6. Ionic Molecules
These are molecules created by ionic bonds between charged particles, known as ions. For instance:
NaCl (Sodium chloride): Sodium ions (Na⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻) create an ionic bond.
7. Covalent Molecules
These are molecules in which atoms share electrons. Most molecules, such as water (H₂O) or carbon dioxide (CO₂), are covalent.
Every molecule has its own role in the natural environment and in all chemical reactions.
You Might Also Like
- How far the electron microscope, increase structures and functions of the organs?
- What is cell: Describe the structure of a plant cell?
- What is Microscope Describe the Parts And Function